

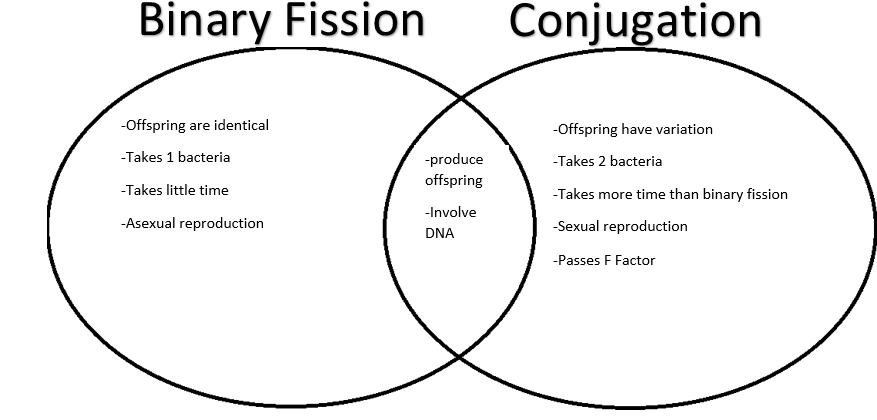
Genes are transferred between bacteria through the pilus. In conjugation, bacteria connect through a protein tube structure called a pilus.Recombination is accomplished in bacterial reproduction by the processes of conjugation, transformation, or transduction. In recombination, genes from one prokaryote are incorporated into the genome of another prokaryote. Genetic variation within prokaryotic organisms is accomplished through recombination. The tubes connecting the bacteria are pili, which are used to transfer genetic material between bacteria. These light-absorbing pigments enable photosynthetic bacteria to obtain nutrition from light.įalse-color transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of an Escherichia coli bacterium (bottom right) conjugating with two other E.coli bacteria. Similar to plants and algae, some prokaryotes also have photosynthetic pigments. This is the layer where bacteria produce biofilm, a slimy substance that helps bacterial colonies adhere to surfaces and to each other for protection against antibiotics, chemicals, and other hazardous substances. Some bacteria also have a polysaccharide capsule layer surrounding the cell wall. Like plant cells, bacteria have a cell wall. According to the Endosymbiotic Theory, eukaryotic organelles are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells living in endosymbiotic relationships with one another. Prokaryotic cells lack organelles found in eukaryoitic cells such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticuli, and Golgi complexes. Nucleoid Region: Area of the cytoplasm that contains the single bacterial DNA molecule.Plasmids: Plasmids are gene-carrying, circular DNA structures that are not involved in reproduction.Ribosomes: Ribosomes are cell structures responsible for protein production.
Flagella: Flagella are long, whip-like protrusions that aid in cellular locomotion.Shorter pili called fimbriae help bacteria attach to surfaces. Pili (Pilus singular): Hair-like structures on the surface of the cell that attach to other bacterial cells.Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane: The cell membrane surrounds the cell's cytoplasm and regulates the flow of substances in and out of the cell.Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules.Cell Wall: The cell wall is an outer covering that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape.Capsule: Found in some bacterial cells, this additional outer covering protects the cell when it is engulfed by other organisms, assists in retaining moisture, and helps the cell adhere to surfaces and nutrients.Using bacteria as our sample prokaryote, the following structures and organelles can be found in bacterial cells: Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes. The most common bacteria shapes are spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral. They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid.
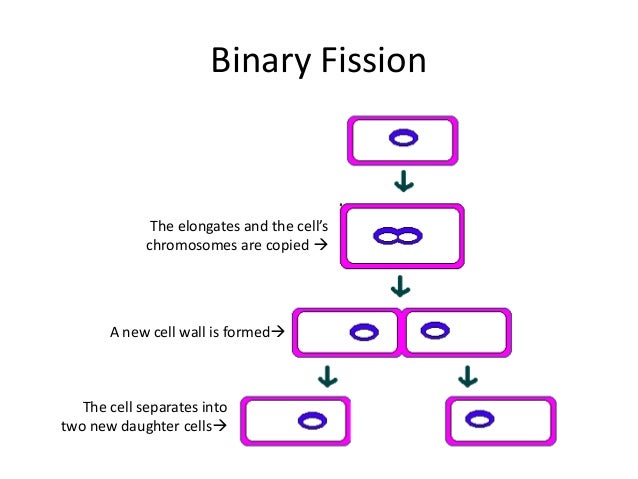
Prokaryotic cells are not as complex as eukaryotic cells. Bacterial Cell Anatomy and Internal Structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
